Yes, Boost Inbox is designed to cater to businesses of all sizes and industries.
.webp)
- What is DNS?
- What is DNSSEC?
- How does DNSSEC work?
- What is DNSSEC Used For?
- Why is DNSSEC Important?
- DNS Record Types and Terms
- How to Implement DNSSEC?
- How to Deploy DNSSEC?
- Benefits of DNSSEC
- How to Set Up DNSSEC for a Domain
- How Does DNSSEC Affect DNS Performance?
- DNSSEC Pros and Cons
- How to Troubleshoot DNSSEC Issues
- DNS vs DNSSEC
- In Summary
- FAQs
- 1. Should I Turn On DNSSEC?
- 2. Do I Need Domain Security?
- 3. What Does DNSSEC Protect Against?
- 4. Why is DNSSEC Not Popular?
- 5. Is Using 8.8.8.8 DNS Safe?
- 6. Why Isn’t Everyone Using DNSSEC?
- 7. What Are DNSKEY and RRSIG Records?
- 8. What Is a Parent Zone and a Child Zone in DNSSEC?
- 9. How Do I Enable DNSSEC?
The internet is like a giant library, and the Domain Name System (DNS) is its catalog. By converting memorable names like "google.com" into computer-understandable numbers known as IP addresses, it helps the process of finding websites. However, what might occur if this catalog was changed? Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) can help with it. It acts as the DNS's kind of security guard, ensuring that no one interferes with the data. We'll look at DNSSEC's definition, functioning, and importance for maintaining internet security in this blog.
What is DNS?
Imagine you want to visit a friend’s house, but you only know their name, not their address. The DNS works similarly to a phone book, looking up their address for you. When you enter a website name into your browser, the DNS locates the correct IP address, allowing your computer to connect to the correct server. For example, when you type "youtube.com," the DNS tells your computer to go to an IP address like 142.250.190.14. Without DNS, we’d have to remember long strings of numbers for every website we visit. DNS is the backbone of internet communication, translating domain names into IP addresses. It also plays an important role in email setup, ensuring that emails reach the correct mail servers without disruption.
But here's the problem: the DNS was developed in the 1980s when the internet was smaller and safer. Back then, no one considered hackers attempting to fool the system. Today, the DNS is subject to assaults such as DNS cache poisoning and man-in-the-middle attacks, which can lead you to fraudulent websites. This is why we need Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC). DNSSEC improves DNS infrastructure security by ensuring secure domain resolution and allowing secure DNS lookup. It serves as a shield, safeguarding users from malicious attacks and keeping the internet a safe place to explore.
What is DNSSEC?
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) improve DNS security by adding cryptographic signatures to DNS records. These digital signature verification methods protect DNS integrity by preventing attacks such as DNS spoofing prevention and domain name hijacking prevention. Think of it like this: if someone sends you a letter, you want to make sure it’s really from them and not a fake. DNSSEC does this for DNS by adding a digital signature to every piece of information. If the signatures match, you know it’s safe to trust.
This method establishes a chain of trust that extends from the root DNS zone to the specified domain. DNSSEC ensures secure domain resolution by verifying each step while also protecting against cache poisoning attacks and man-in-the-middle attacks. In short, DNSSEC works as a security guard for the DNS, ensuring that no one interferes with the data and protecting your online experience.
How does DNSSEC work?
DNSSEC establishes a chain of trust using public key cryptography. When a user sends a DNS query response, DNSSEC-enabled DNS resolvers verify RRSIG records and DNSKEY records to confirm authenticity. This prevents cache poisoning attacks and ensures end-to-end DNS security. Here's how it works, step by step:
Zone Signing: The owner of a website (such as google.com) uses a special key to sign its DNS records. This generates a digital signature that validates the records' authenticity.
Public Key Distribution: The website owner publishes a public key in the DNS. This key works similarly to a master key, allowing digital signatures to be verified.
Chain of Trust: When your computer asks for a website’s IP address, the DNS resolver (the system that searches up the address) verifies the digital signature with the public key. It also verifies with higher-level DNS servers, all the way up to the root zone (at the top of the DNS hierarchy), to ensure that everything is correct.
Validation: If all of the signatures match, the DNS resolver determines that the information is safe to use. If something does not match, it indicates that the data has been interfered with, and the resolver will block it.
This strategy protects DNS integrity and protects against threats such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning.
What is DNSSEC Used For?

Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is used to make the DNS safer and more secure. Here are some of its main jobs:
Preventing DNS Spoofing: DNSSEC stops hackers from redirecting you to fake websites by using DNS authentication to verify the legitimacy of DNS records.
Ensuring Data Integrity: DNSSEC ensures that the DNS information hasn’t been altered. Through DNSSEC validation, it checks the integrity of resource record sets (RRsets), making sure the data is accurate and trustworthy.
Building Trust: By confirming the authenticity of DNS data, DNSSEC helps users feel confident they’re visiting a real website, not a fake one. This is crucial for phishing attack prevention.
Cyber Attack Mitigation: DNSSEC protects against harmful DNS manipulations, such as cache poisoning, enhancing name server security for authoritative DNS servers.
In short, DNSSEC strengthens DNS infrastructure security, ensuring a safer and more reliable internet experience.
Why is DNSSEC Important?
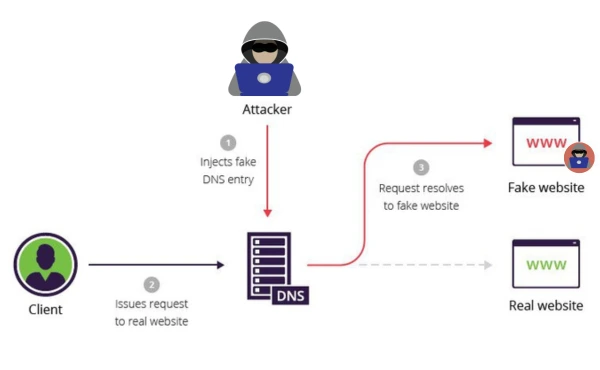
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is like a superhero for the DNS, protecting it from a wide range of threats. Here’s why it’s so important:
1. Trustworthiness of DNS data
Without DNSSEC, hackers can trick the DNS into giving you the wrong IP address. DNSSEC maintains data integrity by using cryptographic signatures and performing a DNS record integrity check. This means you can be confident that the information you receive is correct and wasn't interfered with.
2. Protection against DNS spoofing
DNS spoofing is when hackers send fake DNS information to direct you to unsafe websites. DNSSEC prevents this by verifying the data with digital signatures, ensuring that the DNSSEC trust chain remains strong. This is especially important for DNSSEC-enabled browsers like those with Chrome DNSSEC support and Firefox DNSSEC integration.
3. Data Integrity
DNSSEC ensures that the DNS information has not been changed. DNS integrity is important for the security of the internet. DNSSEC ensures that the data you receive matches what the domain owner published by doing a DNS record integrity check.
4. Phishing Prevention
Phishing is when hackers try to steal your personal information by bringing you into accessing fake websites. DNSSEC helps prevent this by ensuring that you are viewing a real website rather than an illegal one. This is an important part of DNSSEC configuration and is supported by ISP DNSSEC validation.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Benefits
Some businesses, particularly governments and financial institutions, are required by law to use DNSSEC to protect their websites. This ensures they meet regulatory requirements and adds an additional level of security for users.
6. Foundation for Future Security Protocols
DNSSEC is the first step toward creating a safer internet. It protects your data with other security techniques such as Transport Layer Security (TLS). While DNSSEC vs. TLS encryption performs distinct functions, together they form a strong security foundation. DNSSEC, created by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), is a key component for present internet security.
In short, DNSSEC is important for maintaining a secure and trustworthy internet. It protects against attacks, ensures data integrity, and lays the groundwork for future security advancements.
DNS Record Types and Terms
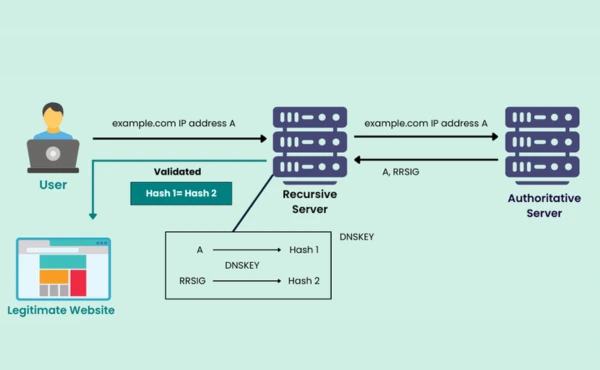
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) require specific DNS records and terms to function effectively. These components support DNS security, data integrity, and secure domain resolution. Here's an overview of the most important ones:
DS Records (Delegation Signer Records)
DS records are important for establishing the chain of trust in DNSSEC. DNSKEY records store a domain's public key, which is used by parent and child DNS zones to authenticate DNS data. Example: if you own "example.com," the DS record in the ".com" zone (parent zone) points to the DNSKEY record in your domain (child zone). This guarantees a secure connection between the two.
DNSKEY Records
DNSKEY records contain public keys used for digital signature verification. These keys are required for verifying the authenticity of DNS data. DNSSEC uses two types of keys: Zone-Signing Key (ZSK) and Key-Signing Key (KSK). DNS resolvers can validate DNS record signatures by using the DNSKEY record, which contains both.
RRSIG Records (Resource Record Signature Records)
RRSIG records contain the cryptographic signatures for DNS data. When a DNS resolver receives a response, it checks the RRSIG record to ensure the data has not been interfered with. This process is a key part of DNSSEC validation and ensures DNS integrity.
RRset (Resource Record Set)
An RRset is a collection of DNS records signed together. For example, all IP addresses linked with a domain name are collected into a RRset and signed as one unit. This makes it easy to manage and validate massive amounts of DNS data.
NSEC and NSEC3 Records
NSEC (Next Secure) and NSEC3 (Next Secure Version 3) records show the absence of a certain DNS record. This prevents attacks like DNS cache poisoning by closing flaws that attackers could use. NSEC 3 improves security by hashing record names, making it more difficult for attackers to guess valid domain names.
Zone-Signing Key (ZSK) and Key-Signing Key (KSK)
DNSSEC uses two types of keys for DNSSEC key management:
- The Zone-Signing Key (ZSK) is used to sign individual DNS records within a zone.
- The Key-Signing Key (KSK) is used to sign the ZSK, creating a secure link between the keys.
These keys are managed through zone file-based DNSSEC, where the keys and signatures are stored in the DNS zone file. Proper DNSSEC deployment requires regular key rotation and secure storage to prevent unauthorized access.
IBM NS1 Connect
IBM NS1 Connect is a powerful DNS management platform that supports DNSSEC deployment. It simplifies the process of configuring and managing DNSSEC, making it easier for organizations to implement DNS security and protect their domains. With tools like IBM NS1 Connect, businesses can automate DNSSEC key management, ensure digital signature verification, and maintain a secure chain of trust.
MX Records (Mail Exchange Records)
An MX record (Mail Exchange record) is a type of DNS record that specifies the mail servers responsible for receiving emails on behalf of a domain. Configuring MX records correctly is essential for a new email domain, ensuring smooth email delivery.
How to Implement DNSSEC?
When implementing DNSSEC, it's important to secure key DNS records, including MX records, to protect against spoofing and phishing attacks. Additionally, ensuring that your Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) supports DNSSEC can help prevent email delivery failures. Implementing Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) involves a few key steps to secure your DNS zone and protect your domain from attacks. Here’s a simple guide to get started:
Select a DNSSEC-Compatible DNS Provider: Not all DNS providers support DNSSEC, so select one that offers DNS zone signing and automated DNSSEC signing features. Popular companies such as Cloudflare, Google Cloud DNS, and IBM NS1 Connect are excellent choices.
Generate your keys (ZSK and KSK): Create two types of cryptographic keys, Zone-Signing Key (ZSK) and Key-Signing Key (KSK). These private key pairs sign your DNS records and create a secure chain of trust.
Sign Your DNS Zone: Use your DNS provider’s tools to sign your DNS zone. The process provides cryptographic signatures to your DNS records, ensuring authenticity and integrity.
Publish Your DS Record: After signing your zone, publish your Delegation Signer (DS) record with your domain registrar. This record connects your domain to your public key and enables DNSSEC validation.
Monitor and Maintain: Regularly check your DNSSEC configuration to ensure keys are secure and up-to-date. Automated tools improve DNSSEC key management and maintenance.
By following these steps, you can enable DNSSEC configuration and improve your domain’s security, protecting it from threats like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning.
How to Deploy DNSSEC?
The deployment of Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is similar to its implementation. Begin by collaborating with your DNS provider and domain registrar to create Delegation Signer (DS) records that connect your domain to its public key. Many providers provide tools for simplifying the process, such as OpenDNSSEC implementation or the Secure64 appliance.
These solutions automate authoritative DNS server security, ensuring that your DNS zone is correctly signed and confirmed. You can implement DNSSEC easily by working with your provider and registrar to improve your domain's protection against attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning.
Benefits of DNSSEC
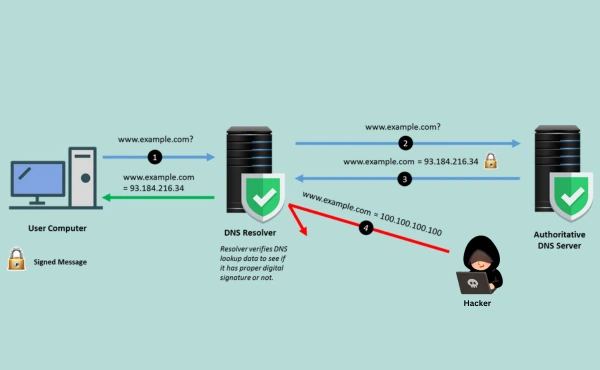
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) offer numerous benefits that strengthen DNS infrastructure security and protect users. Here are the key advantages:
Enhanced Security: DNSSEC improves security by protecting against threats such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, providing secure domain resolution, and preventing man-in-the-middle attack protection.
Improved Trust: By verifying DNS record integrity, DNSSEC assures that users are visiting the correct website rather than an unauthorized one, boosting confidence in your domain.
Compliance: DNSSEC improves authoritative DNS server security, which helps businesses meet legal requirements, particularly in banking and government.
In short, DNSSEC is a vital tool for cyber attack mitigation and website security enhancement.
How to Set Up DNSSEC for a Domain
Setting up Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) for your domain is a straightforward process that enhances DNS infrastructure security. Before enabling DNSSEC, it’s advisable to check your email sending limits. Some email providers enforce restrictions on domains that don’t have proper DNS configurations, which can affect the reliability of outgoing emails. Here’s how to do it:
Enable DNSSEC with your DNS provider: Start by configuring DNSSEC through your DNS provider. Many providers, including those supporting BIND 9.7 DNSSEC configuration, offer built-in tools to simplify this step. Platforms like Micetro by Men&Mice also provide DNS security automation tools to streamline the process.
Generate and Manage Your Keys: Create and manage your cryptographic keys, including the Zone-Signing Key (ZSK) and Key-Signing Key (KSK). These keys are essential for signing your DNS records and ensuring DNS record integrity.
Publish Your DS Record: Once your DNS zone is signed, publish the Delegation Signer (DS) record with your domain registrar. This record connects your domain with its public key, ending the chain of trust.
By following these steps, you can secure your domain against threats like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, ensuring a safer online experience for your users.
How Does DNSSEC Affect DNS Performance?
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) may lead to some delay in DNS queries due to the additional processes necessary for digital signature verification. This involves checking for cryptographic key expiration and confirming the chain of trust. While this may have a minor performance impact, the additional security is well worth it.
For dynamic DNS zones, where records change often, proper key management and automation tools can help to reduce delays. Overall, DNSSEC's benefits in avoiding DNS spoofing and ensuring DNS integrity outweigh the slight speed impact.
DNSSEC Pros and Cons
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) offers significant benefits but also comes with a few challenges. Here’s a quick look at the pros and cons:
Pros:
- Protects Against DNS Attacks: DNSSEC safeguards against threats like DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, ensuring secure domain resolution.
- Ensures Data Integrity: By using DNS encryption and digital signature verification, DNSSEC guarantees that DNS data hasn’t been tampered with.
- Builds User Trust: With DNSSEC-enabled browsers like Chrome and Firefox, users can trust they’re visiting legitimate websites.
Cons:
- Complex Setup: DNSSEC key management and the zone resigning process can be technically challenging, especially for large or dynamic DNS zones.
- Small Delay: The extra steps for validation may add a slight delay to DNS queries, though the impact is usually minimal.
Despite its complexities, DNSSEC is a powerful tool for enhancing DNS infrastructure security and protecting users.
How to Troubleshoot DNSSEC Issues
Common Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) issues include mismatched keys and expired signatures, which are frequently triggered by DNSSEC key management or zone resigning process. To fix these issues, first check that your Zone-Signing Key (ZSK) and Key-Signing Key (KSK) are properly configured.
If your DNS zone's signatures have expired, re-sign it with the tools provided by your DNS provider. To simplify the process of managing dynamic DNS zones, explore using automation tools. Regularly checking your DNSSEC settings may help prevent issues and keep your DNS infrastructure secure.
DNS vs DNSSEC
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the internet's backbone, converting human-readable domain names such as "example.com" into machine-readable IP addresses. However, DNS lacks built-in security, leaving it open to attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning. This is where DNSSEC comes in. DNSSEC is a DNS extension that improves security by adding cryptographic signatures to DNS records. These signatures secure DNS integrity and prevent interference, keeping the internet safer for all. In short, DNS allows the internet to function, while DNSSEC ensures its security.
In Summary
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) are an important tool for keeping the internet safe and secure. It safeguards against attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, guaranteeing secure domain resolution and preserving DNS integrity. DNSSEC increases domain name security and trust by including cryptographic signatures in DNS records, ensuring that users are directed to genuine sites.
While configuring DNSSEC can be difficult, particularly with work such as DNSSEC key management and zone resignation, the advantages of a safer and more reliable internet far outweigh the difficulties. DNSSEC is a key component of modern DNS infrastructure security, making it an important tool for safeguarding online interactions.
FAQs
1. Should I Turn On DNSSEC?
Yes, turn on Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) to improve DNS infrastructure security. It adds cryptographic signatures to DNS records to ensure secure domain resolution and protect against DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks. Required for domain name security and user trust.
2. Do I Need Domain Security?
Absolutely! Domain security is important for preventing domain name hijacking and other online threats. Without it, attackers can send users to fake websites or steal important data. DNSSEC is an important tool for protecting your domain and ensuring DNS integrity.
3. What Does DNSSEC Protect Against?
DNSSEC protects against a variety of threats, including cache poisoning and man-in-the-middle attacks. It ensures that the DNS data you receive is genuine and has not been tampered with, leading to secure DNS lookups and improved end-user security.
4. Why is DNSSEC Not Popular?
DNSSEC's complexity and DNSSEC configuration challenges prevented its adoption. Many businesses struggle to implement DNSSEC key management and the zone resigning process. Additionally, delayed ICANN DNSSEC implementation and a lack of awareness have contributed to its limited popularity.
5. Is Using 8.8.8.8 DNS Safe?
Google's public DNS (8.8.8.8) provides limited DNSSEC validation but does not fully enforce DNSSEC. While typically safe, selecting a DNS provider that fully supports DNSSEC is advised for whole DNS infrastructure security.
6. Why Isn’t Everyone Using DNSSEC?
The slow adoption of DNSSEC is due to its complexity, implementation hurdles, and the need for DNSSEC-enabled browsers and tools. Many organizations also lack the technical skills required to manage DNSSEC keys and maintain the DNSSEC trust chain.
7. What Are DNSKEY and RRSIG Records?
DNSKEY records hold the public keys required for digital signature verification, while RRSIG records contain the cryptographic signatures for DNS data. Together, they guarantee the reliability and integrity of resource record sets (RRsets).
8. What Is a Parent Zone and a Child Zone in DNSSEC?
In DNSSEC, a parent zone (like .com) gives authority to a child zone. This structure is part of the parent and child DNS zone system, helping in the creation of a chain of trust for secure DNS data transfer.
9. How Do I Enable DNSSEC?
To enable DNSSEC, verify with your domain registrar and follow their instructions. To set up the DNSSEC trust chain, you must first generate keys, sign your DNS zone, and publish your Delegation Signer (DS) record. Many providers offer tools to simplify DNSSEC configuration and DNS security automation.
What to read next
Absolutely! Boost Inbox is compatible with most major email service providers.
The warmup process duration may vary depending on your email volume, but it typically ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks.
Yes, Boost Inbox offers dedicated customer support to assist you throughout the warmup process.
While it's possible, it's best to start the warmup process from the beginning with Boost Inbox for optimal results.

