Yes, Boost Inbox is designed to cater to businesses of all sizes and industries.

- What Is a Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)?
- How Does a Mail Transfer Agent Work?
- Key Functions of a Mail Transfer Agent
- Mail Transfer Agent Examples
- On-premises Vs. Cloud-based Mail Servers
- Using MTA for Email Marketing
- How Do You Select the Right MTA?
- How Do Mail Transfer Agents Affect Email Deliverability?
- How are Mail Transfer Agents used in email marketing?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- 1. What does a transfer agent do?
- 2. What is an example of a transfer agent?
- 3. What is the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) process?
- 4. Is Gmail a mail transfer agent?
- 5. What are the phases of mail transfer?
- 6. What is the difference between Sendmail and SMTP?
- 7. What is the difference between MTA, MDA, & MUA?
- 8. Which protocol is used for transferring mail?
- 9. What is MUA (Mail User Agent)?
- 10. What is an MSA (Mail Submission Agent)?
- 11. What is MTA (Mail Transfer Agent)?
- 12. What is an MDA (Mail Delivery Agent)?
- 13. What is SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)?
- 14. What is MX Records (Mail Exchange Records)?
Imagine writing an important letter to a loved one, carefully sealing it, and hoping it would reach them. Behind the scenes, the postal service guarantees that your mail is delivered safely. In the digital world, a Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) does the same thing with your emails. It's the invisible force that transports your words across the internet, ensuring that they arrive in the correct inbox.
But what exactly defines an MTA? How does it move the wide web globe and deliver your emails? Why does it matter, especially when billions of emails are transmitted every day? In this blog, we'll explain what is a mail transfer agent and the magic of MTAs in simple, understandable terms. Whether you're thinking about how emails function or want to avoid losing messages, this guide will help you understand the hidden hero of email delivery.
What Is a Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)?
A Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) is a type of software that transfers emails from one computer to another. It performs an important function in the Electronic Mail System, ensuring that emails are delivered to the correct location. Consider it similar to a mailman who collects letters and delivers them to their proper addresses.
When you send an email, the MTA uses the Mail Transfer Protocol to move it from your email service to the recipient's email server. It works as a middleman, providing Mail Server Communication between multiple servers. Without an MTA, emails would be unable to move across the internet.
An MTA is also called a Mail Transport Agent, Message Transfer Agent, or Mail Server MTA. It is an essential part of the Email Infrastructure, making sure that all emails are delivered quickly and securely to the right inbox.
How Does a Mail Transfer Agent Work?
To understand how an MTA works, we'll go through the email delivery process step by step. Emails do not simply appear in someone's mailbox; they go through a sequence of phases, each handled by a distinct component. First, your email is routed to a Mail Submission Agent (MSA), who confirms that it is properly prepared. Next, the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) takes over. It uses Mail Exchange (MX) Records to locate the recipient's email server, a process known as email routing. The MTA then routes your email through an email relay system, moving it from one server to the next until it reaches its destination.
This entire process is part of the email delivery mechanism, ensuring your message is delivered safely and efficiently. MTAs use the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to relay emails between servers. Proper SMTP Configuration ensures smooth email delivery and prevents issues like email bouncing or failed transmissions.
MTA in the Email Delivery Process
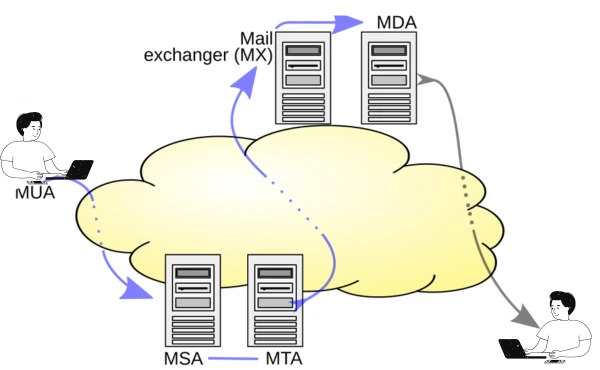
To understand how an MTA works, we'll go through the email delivery process step by step. Emails don’t just magically appear in someone’s inbox they go through a series of stages, each handled by different components. The MTA uses email protocols like SMTP for email traffic management, ensuring your message moves smoothly. If the recipient's server is busy, it keeps emails in an email queue and serves as a mail relay, routing your email from one server to another until it arrives at its destination. This method ensures that your email is delivered continually, even when the internet is busy.
Mail User Agent (MUA)
The Mail User Agent (MUA) is the email client software you use to write, read, and send emails. Think of it as the app or program, like Gmail, Outlook, or Apple Mail, that lets you type your message and hit “send.” It’s like the pen and paper you use to write a letter. The MUA also helps you organize your inbox and add important details, like email headers and metadata, which include information about the sender, recipient, and subject line.
Mail Submission Agent (MSA)
Once you hit “send,” your email is passed to the Mail Submission Agent (MSA). This component is part of the email submission process and ensures your email is properly formatted and ready for delivery. It checks for errors, like missing addresses, and prepares the email for the next step. The MSA acts as a gatekeeper, making sure everything is in order before handing it off to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA).
Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)
The Mail Transfer Agent (MTA), also known as the Mail Transport Agent Linux in some systems, is the real workhorse of email delivery. It takes the email from the MSA and figures out how to deliver it. Using the recipient’s email address, the MTA determines the correct mail server through message routing in emails. It acts as an SMTP relay service, passing the email from one server to another until it reaches the right destination. If the recipient’s server is busy, the MTA stores the email in a queue and tries again later.
Mail Delivery Agent (MDA)
Finally, the Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) takes over. This component is responsible for delivering the email to the recipient’s inbox. It’s like the mail carrier who drops the letter into your friend’s mailbox. The MDA ensures the email is stored correctly and can be accessed by the recipient’s email client software. Examples of MDAs include programs like Procmail or Dovecot, which are mail delivery agent examples used in many email systems. Together, these components ensure your email travels smoothly from your outbox to the recipient’s inbox.
Store-and-Forward Model of Email Handling
MTAs use a store-and-forward email system to handle emails. This means they temporarily hold your email, determine the best way to deliver it, and then forward it to the next server in the chain. If the recipient's server is unavailable, the MTA will proceed with deferred email processing until the email is delivered or bounced. This prevents your email from being lost, even if there are temporary issues along the way.
MTA and SMTP Relay
MTAs rely on the SMTP protocol to send emails. Think of SMTP as the language MTAs use to communicate with each other. When an MTA sends an email, it acts as an SMTP relay service, passing the message from one server to another using TCP/IP email transmission. This email relaying mechanism ensures your email travels securely and efficiently until it reaches its destination.
Key Functions of a Mail Transfer Agent
MTAs perform several important tasks to ensure smooth email delivery. Here are some of their key functions explained in detail:
Accepting Emails from MUAs
The first job of an MTA is accepting emails from MUAs (Mail User Agents). When you hit “send” in your email client, like Gmail or Outlook, the MTA takes over. It starts the email submission process by receiving your email and preparing it for delivery. Think of it as a post office accepting your letter and getting it ready for the journey.
Selecting Target Mail Server
Once the MTA has your email, it must determine where to send it. Choosing the appropriate mail server is important here. The MTA uses the recipient's email address and looks up DNS MX Records (Mail Exchange Records) to locate the appropriate server. The MTA finds the best route for your email to reach its destination during the email routing process.
Sending Auto-Responses for Failed Delivery
Sometimes emails cannot be delivered. Maybe the recipient's email address does not exist, or the server is offline. When this happens, the MTA automatically sends a non-delivery report (NDR) or a bounce email to the sender. This notifies you that something went wrong so you can solve it.
Queueing Emails
If the recipient’s server is busy or unavailable, the MTA doesn’t give up. Instead, it stores your email in a mail queue, which is part of the email queuing system. The MTA attempts to send the email at regular intervals until it succeeds or concludes it is undeliverable. This ensures that your email is not lost, even if there is a temporary issue.
Controlling Sending Rate (Throttling)
Sending too many emails at once can overload the recipient's server. To prevent this, the MTA uses email throttling to regulate the rate at which emails are delivered. This allows smooth email traffic management and removes server overload.
Managing Connections
The MTA manages connections between servers. SMTP connection management ensures secure connection establishment, maintenance, and closure. This ensures that emails are properly and quickly transmitted between servers.
Transferring Email Data
The MTA ensures proper email transmission, including content, attachments, and headers. This process, known as email transmission, ensures that your message is intact and readable.
Processing Delivery Deferrals
If an email is temporarily undeliverable, the MTA does not give up right away. Instead, it uses deferred email processing to resend the message later. This is especially beneficial when the recipient's server is temporarily unavailable or busy.
Generating Bounce Messages
When an email cannot be delivered, the MTA sends a bounce message to the sender. This is part of email bounce handling, which explains why the email failed and how to resolve it.
Monitoring Delivery Status
Finally, the MTA tracks whether your email was delivered properly or bounced. Monitoring delivery status enables the MTA to better manage email traffic and optimize future delivery. By tracking delivery status, the MTA guarantees that your emails get at their destination as smoothly as possible.
Mail Transfer Agent Examples

There are several MTAs available, each with its features:
1. Exim
Exim is a highly flexible and powerful mail transfer agent (MTA) known for its extensive configuration options. It is widely used for Exim mail server setups and is capable of handling Exim SMTP relay tasks efficiently.
Features:
- Supports advanced email routing and spam filtering.
- Highly customizable for complex email systems.
- Open-source and free to use.
- Handles email queuing and bounce messages effectively.
- Ideal for system administrators who need flexibility.
2. Postfix
Postfix is a popular MTA designed for efficiency and security. It is often used in Postfix mail server configurations and is known for its speed and reliability.
Features:
- Easy to configure compared to other MTAs.
- Supports SMTP authentication and email encryption.
- Uses DNS MX records for proper email routing.
- Highly scalable for both small and large businesses.
- Built-in spam filtering and email queuing capabilities.
3. Sendmail
Sendmail is one of the oldest and most robust MTAs available. It is known for its Sendmail configuration flexibility and ability to handle complex Sendmail email server setups.
Features:
- Highly scalable for large email volumes.
- Supports advanced email routing and SMTP relay.
- Customizable for complex email systems.
- Reliable and trusted for enterprise-level use.
- Requires expertise in configuration and management.
4. Microsoft Exchange Server
Microsoft Exchange Server is a comprehensive email solution used primarily in corporate environments. It integrates email, calendaring, contacts, and task management into one platform.
Features:
- Seamless integration with Microsoft Outlook and other Microsoft tools.
- Advanced email encryption and spam filtering.
- Supports email forwarding and DNS MX records.
- User-friendly interface for businesses.
- Ideal for organizations using Microsoft products.
5. Qmail
Qmail is a secure and simple mail transfer agent known for its focus on security. It is part of the Qmail mail transfer system and is designed to be lightweight and efficient.
Features:
- Easy to configure and manage.
- Focuses on security and reliability.
- Supports SMTP relay and email queuing.
- Handles bounce messages and deferred email processing.
- Lightweight and efficient for small to medium setups.
6. Axigen
Axigen is a powerful mail server MTA that offers integrated email, calendaring, and collaboration services.
Features:
- Supports email encryption and spam filtering.
- Offers webmail and mobile access for remote users.
- Handles email forwarding and DNS MX records.
- User-friendly interface for businesses.
- Ideal for organizations needing a comprehensive communication solution.
7. Mutt
Mutt is a text-based mail user agent (MUA) that also includes MTA capabilities. It is lightweight and fast, making it a popular choice for users who prefer simplicity.
Features:
- Lightweight and efficient for quick email handling.
- Supports email queuing and SMTP relay.
- Highly customizable for advanced users.
- No graphical interface, but highly efficient for developers.
- Ideal for users who prefer command-line tools.
8. OpenSMTPD
OpenSMTPD is a secure and simple MTA that is part of the OpenBSD project. It is designed with a focus on security and ease of use.
Features:
- Simple and easy to configure.
- Supports SMTP authentication and email encryption.
- Uses DNS MX records for proper email routing.
- Lightweight and efficient for personal and business use.
- Focuses on security and reliability.
9. Postal
Postal is an email server designed for handling large volumes of email efficiently.
Features:
- Supports email queuing and SMTP relay.
- Handles bounce messages and deferred email processing.
- Highly scalable for businesses with high email traffic.
- Customizable for specific email needs.
- Ideal for bulk email sending and large-scale operations.
10. Amazon SES (Simple Email Service)
Amazon SES is a cloud-based mail transfer agent designed for sending bulk emails.
Features:
- High deliverability and scalability for bulk emails.
- Supports email encryption and SMTP authentication.
- Provides email tracking and analytics.
- Cost-effective for businesses sending large volumes of emails.
- Integrates seamlessly with other Amazon Web Services (AWS).
11. Alpine
Alpine is a fast and easy-to-use mail user agent (MUA) that also includes MTA capabilities.
Features:
- Lightweight and efficient for quick email handling.
- Supports email queuing and SMTP relay.
- User-friendly interface for beginners.
- Ideal for personal and small business use.
- No advanced features but highly efficient for basic needs.
12. Mailgun
Mailgun is a powerful mail transfer agent that provides APIs for sending, receiving, and tracking emails.
Features:
- Supports email encryption and SMTP relay.
- Provides email tracking and analytics.
- Ideal for developers integrating email functionality into apps.
- Scalable for businesses of all sizes.
- Easy-to-use APIs for seamless integration.
13. SendGrid
SendGrid is a cloud-based mail transfer agent that specializes in email delivery and marketing services.
Features:
- Supports email encryption and SMTP authentication.
- Provides advanced analytics for email campaigns.
- Ideal for businesses sending bulk emails.
- User-friendly interface for marketing teams.
- High deliverability and scalability for large email volumes.
On-premises Vs. Cloud-based Mail Servers
When choosing an MTA, you’ll need to decide between on-premises and cloud-based mail servers.
On-premise Mail Servers
On-premises mail servers are hosted on your hardware, giving you full control over your email server configuration and security. You are responsible for everything, from server setup to server maintenance. This is excellent for enterprises that require full control over their email infrastructure. However, it requires significant resources, like IT staff and equipment, and can be expensive to maintain.
Cloud-based Mail Servers
Cloud-based mail servers are hosted by third-party providers such as Amazon Simple Email Service (SES), Mailgun Email API, and SendGrid Email Delivery. These services manage all technical aspects, so you won't have to bother about hardware or maintenance. They provide scalability, dependability, and ease of use, making them suitable for enterprises of all sizes. Other examples include Mailjet SMTP Server and Proofpoint Email Security, which offer extra capabilities such as email tracking and better security. Cloud-based servers are ideal for corporations seeking a hassle-free email solution.
Using MTA for Email Marketing

Mail Transfer Agents play a crucial role in email marketing, ensuring that promotional and transactional emails reach recipients reliably. Here’s how MTAs support marketing efforts:
Executing Promotional Campaigns
MTAs are important for executing promotional campaigns because they handle bulk email sending efficiently. Whether you're sending thousands of emails for a product launch or a holiday sale, MTAs ensure that your messages arrive swiftly and reliably. They maintain email infrastructure to ensure timely delivery to the intended audience. This makes MTAs the foundation of email marketing campaigns.
Sending Drip Campaigns
MTAs also play a key role in sending drip campaigns, which are automated email sequences like welcome series, follow-ups, or reminders. These campaigns require email forwarding and scheduling, which MTAs perform easily. For example, if a user subscribes to your newsletter, the MTA can automatically send a welcome email and follow-up messages at scheduled times. his automation saves time and ensures consistent communication with your audience.
Tracking and Analytics
One of the most valuable features of MTAs is their ability to provide tracking and analytics. They monitor email traffic management, giving you insights into how your emails are performing. Metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and bounce rates can assist you in determining what works and what doesn't. This information is important for optimizing your email marketing strategies and getting better outcomes.
Reliable Delivery
MTAs ensure reliable delivery by optimizing the email delivery process. They act as a mail transport agent, routing emails through optimal routes to prevent delays and failures. MTAs help emails bypass spam filters and reach the recipient's inbox instead of the spam folder. This dependability is important to the success of any email marketing strategy.
Email Authentication
To protect your emails from being marked as spam or phishing attempts, MTAs support email authentication protocols like DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), Sender Policy Framework (SPF), and Domain-based Message Authentication (DMARC). These techniques ensure that your emails come from a genuine source, which boosts confidence and improves delivery. This is very important for keeping your sender's reputation.
Integration with CRM
MTAs can integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) tools, allowing you to create personalized email campaigns. Connecting your MTA to your CRM allows you to use customer data to send targeted emails based on user activity, preferences, or demographics. This integration enhances the effectiveness of your campaigns and improves engagement rates. Additionally, MTAs work seamlessly with email client software, ensuring a smooth experience for both senders and recipients.
How Do You Select the Right MTA?
Choosing the right Mail Transfer Agent depends on multiple factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Assess Your Requirements
The first step in choosing the right Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) is to assess your requirements. Do you send transactional emails like password resets or order confirmations, or marketing emails like newsletters and promotions? Your needs will determine the best MTA for your email infrastructure. For example, if you’re sending bulk emails, you’ll need an MTA that specializes in bulk email handling. Understanding your goals will help you narrow down your options and choose the right mail transport agent.
Research Available Options
Once you know your requirements, the next step is to research available options. Compare on-premises MTAs like Postfix and Sendmail with cloud-based solutions like Mailgun and Amazon SES. Explore mail transfer agent examples and mail transfer agent lists to evaluate the pros and cons of each option. Postfix offers customization, while Amazon SES focuses on scalability. Researching thoroughly will help you make an informed decision.
Evaluate Features and Functionality
When choosing an MTA, it's important to consider features and functionality. Does the MTA support email protocols, like SMTP, IMAP, and POP3? Does it support queue management, auto-retries, and email security protocols? SendGrid provides powerful statistics, whereas Exim allows for extensive customization. Make sure the MTA you choose has the features you need to manage your email system effectively.
Consider Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority when choosing an MTA. Look for features like TLS encryption for emails, spam filtering, and email encryption. Additionally, ensure the MTA complies with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA if you’re handling sensitive data. For example, Microsoft Exchange Server offers robust email security compliance, making it a great choice for businesses that prioritize data protection. A secure MTA will safeguard your emails from possible hackers while also ensuring legal compliance. When selecting an MTA, it’s important to ensure that it aligns with security best practices, especially if you are setting up a new email domain. Proper configuration helps in preventing unauthorized access and improving email deliverability.
Evaluate Performance and Reliability
When selecting an MTA, it is important to consider reliability as well as performance. Evaluate the MTA's uptime, email transmission speed, and mail server communication efficiency. Postfix is known for reliability, while Amazon SES has great delivery rates. A solid MTA guarantees that your emails arrive on schedule and without interruptions, which is important in maintaining confidence with your recipients.
Consider Integration and Compatibility
Your MTA should integrate effortlessly with your current tools and processes. Ensure it supports your email client software, such as Gmail or Outlook, and interfaces with APIs if necessary. Mailgun is a popular choice among developers due to its easy connection with multiple platforms. Compatibility with your current email setup will save you time and effort in the long run.
Assess Support and Documentation
Good support and documentation are important for troubleshooting and configuration. Look for MTAs with well-documented guidelines and strong support communities. For example, Postfix and Exim have extensive documentation and community forums. If you’re using a mail transport agent Linux system, ensure the MTA has clear instructions for installation and configuration. Reliable support will help you resolve issues quickly and keep your email system running smoothly.
Trial and Testing
Before committing to an MTA, take advantage of free trials or testing periods. Most cloud-based MTAs, like SendGrid and Amazon SES, offer free tiers to test email delivery and performance. Use this opportunity to evaluate how well the MTA meets your needs. Testing will help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure you choose the right solution.
Cost Considerations
Finally, evaluate the expense of the MTA. Some MTAs, such as Postfix and Exim, are free and open-source, making them suitable for budget-conscious consumers. Others, such as Amazon SES and SendGrid, offer subscription-based pricing. Choose an MTA that is within your budget and has the scalability you require. Consider a cloud-based solution for bulk email handling to save money in the long run.
How Do Mail Transfer Agents Affect Email Deliverability?
Mail Transfer Agents (MTAs) play an important role in ensuring your emails reach the recipient’s inbox. They manage the entire email delivery process, from sending to monitoring, and help improve email deliverability. Here’s how MTAs make a difference:
Sender Reputation Protection
MTAs play an important role in ensuring email delivery by protecting sender reputation. Your sender reputation is similar to a report card that Internet Service Providers (ISPs) use to determine whether your emails should be sent to the inbox or the spam folder. MTAs manage email traffic properly, gaining a positive reputation. They ensure that you don't send too many emails at once, which can activate spam filters. MTAs monitor email activity to prevent IP whitelisting/blacklisting issues. For example, if your IP address is recognized as sending spam, your emails may be restricted. MTAs safeguard and improve email sender reputation by regulating email traffic and assuring compliance with email best practices.
Warming Up IP Addresses
MTAs assist in warming up new IP addresses when sending emails. This involves progressively raising the number of emails you send to create confidence with ISPs. If you send a huge volume of emails all at once from a new IP address, it may appear suspicious and damage your sender reputation. MTAs automate the process by gradually increasing your email volume over time. This identifies your IP as trustworthy and ensures that your emails are delivered to your inbox. Warming up your IP address is important for effective email traffic management and avoiding spam filters.
Managing Sending Rate
MTAs are responsible for maintaining email sending rate, or speed. Sending too many emails too rapidly may overload recipient servers as well as turn up spam filters. MTAs use email throttling to control sending rates and maintain a consistent and controllable flow of emails. This not only keeps your emails from being marked as spam, but it also protects your sender reputation. For example, if you’re sending a large marketing campaign, the MTA will distribute the emails over time instead of sending them all at once. This careful management of email traffic ensures your emails reach their destination without issues.
Bypassing Graylists
Recipient servers may use graylisting to temporarily block emails from unknown senders. This is a safety measure to prevent spam. MTAs help bypass graylists by automatically retrying to send the email after a short delay. When the MTA retries, the destination server recognizes it as a legitimate sender and permits the email to pass. This step is part of postponed email processing and prevents emails from being permanently blocked. By handling graylisting effectively, MTAs improve your email deliverability and ensure your messages reach the inbox.
Setting Email Throttling Rules
MTAs use email throttling rules to prevent overloading recipient servers. Throttling controls the quantity of emails sent each hour or minute, maintaining a consistent and continuous flow. This is particularly important for large email campaigns, as sending too many emails at once might result in delays or bounces. MTAs also alter throttling based on the recipient server's capacity, ensuring that your emails are delivered effectively. Proper email throttling improves delivery and protects sender reputation by avoiding spam filtering.
Routing Guidelines
MTAs use routing standards to ensure emails are delivered to the correct recipient. DNS MX Records help identify the recipient's mail server and route emails accordingly. Message routing in emails ensures emails take the most efficient way to the inbox. MTAs may also handle advanced routing scenarios, such as when the recipient's server is down or unavailable. MTAs optimize email routing to ensure consistent and on-time delivery.
Monitoring Outgoing Mail
MTAs regularly monitor outgoing mail to maintain seamless operations. They monitor metrics like as email delivery rates, bounce rates, and open rates to detect potential problems. Email traffic management provides insight into email performance and identifies areas for improvement. For example, if a large volume of emails are bouncing, the MTA will notify you to resolve the problem. y keeping a close eye on your email activity, MTAs help you maintain high deliverability and improve your email campaigns.
Handling Bounces and Deferrals
MTAs are important for managing bounces and deferrals, which occur when emails cannot be delivered. Bounces happen when an email address is incorrect or the recipient's server is unavailable. Deferrals happen when the recipient's server is temporarily offline. MTAs address these challenges by deferred email processing and retrying to send it later. They also send bounce emails to notify you of delivery difficulties. MTAs increase email deliverability by successfully managing bounces and deferrals, ensuring that messages reach their intended recipients.
How are Mail Transfer Agents used in email marketing?
MTAs are important tools for email marketing. They enable bulk email sending, ensure spam filtering and security, automate follow-ups, and provide detailed analytics. These features make MTAs indispensable for businesses looking to maximize the impact of their email campaigns.
Bulk Email Sending
Businesses use MTAs for bulk email sending, including promotional, newsletter, and transactional emails. Whether you're operating a large marketing campaign or sending order confirmations, MTAs ensure that your emails get delivered quickly. They handle email forwarding and delivery, ensuring timely transmission to large numbers of recipients. This capacity is important for businesses that need to communicate with large audiences quickly and reliably.
Spam Filtering & Security
MTAs play an important role in ensuring your emails pass through spam filtering and security checks. To prevent spam, emails are verified using protocols such as SMTP authentication, DNS MX records, and email encryption. MTAs contribute to sender reputation and deliverability by verifying that your emails meet security standards. This is particularly important for businesses that send a large number of emails and want to avoid being flagged by spam filters.
Automated Follow-Ups
MTAs allow organizations to deliver automated follow-ups, including drip campaigns and customized messaging. For example, if a customer registers for your service, the MTA can send a welcome email and follow-up messages at regular intervals. This automation saves time while ensuring continuous communication with your audience. MTAs provide seamless email forwarding and delivery, boosting follow-up and customer engagement.
Detailed Analytics
MTAs offer precise data to track the performance of email campaigns. Metrics including as open rates, bounce rates, and delivery success rates provide useful information about how your emails function. This data helps you identify areas for improvement and optimize your ads for better outcomes. By providing real-time tracking and reporting, MTAs enable businesses to make data-driven decisions and meet their email marketing goals.
Conclusion
A Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) is the foundation of email communication, ensuring that emails are reliably sent and delivered. Whether you're a corporation sending bulk emails or an individual sending personal messaging, an MTA is important for email transmission, security, and delivery. With options ranging from on-premises MTAs like Postfix and Exim to cloud-based services like Amazon SES and SendGrid, selecting the right MTA depends on your demands, price, and security requirements. Understanding how MTAs work and their importance in email infrastructure allows you to make informed decisions about how your emails are delivered effectively and securely.
FAQs
1. What does a transfer agent do?
A Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) handles the delivery of emails from one server to another. It ensures your emails are routed correctly and delivered to the recipient’s inbox. Think of it as the postal service of the internet, managing the entire email transmission process.
2. What is an example of a transfer agent?
Examples of Mail Transfer Agent Examples include Postfix, Exim, and Sendmail. These are software programs that manage the transfer of emails between servers. Each has its features, like Sendmail Configuration flexibility or Postfix’s focus on security.
3. What is the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) process?
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the language MTAs use to send and receive emails. It’s part of the SMTP Relay Service, which ensures emails are passed from one server to another until they reach their destination. SMTP is essential for email delivery.
4. Is Gmail a mail transfer agent?
No, Gmail is not an MTA. It’s an email client (MUA) that you use to send and receive emails. However, Gmail Email Infrastructure uses MTAs behind the scenes to handle the actual delivery of emails.
5. What are the phases of mail transfer?
The phases of mail transfer include:
Email Submission Process: When you hit “send,” your email is submitted to the MSA.
Email Transmission: The MTA transfers the email between servers using SMTP.
Email Delivery: The MDA delivers the email to the recipient’s inbox.
6. What is the difference between Sendmail and SMTP?
Sendmail is a specific Mail Transfer Agent (MTA), while SMTP is the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol used by MTAs to send emails. In other words, Sendmail is the software, and SMTP is the language it uses to communicate.
7. What is the difference between MTA, MDA, & MUA?
Mail Transfer Agent (MTA): Transfers emails between servers.
Mail Delivery Agent (MDA): Delivers emails to the recipient’s inbox.
Mail User Agent (MUA): The email client (like Gmail or Outlook) you use to send and receive emails.
8. Which protocol is used for transferring mail?
The Mail Transfer Protocol used for transferring mail is the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). It’s the standard protocol for sending emails across the internet.
9. What is MUA (Mail User Agent)?
A Mail User Agent (MUA) is the email client you use to write, send, and read emails. Examples include Gmail, Outlook, and Apple Mail. It’s the interface you interact with to manage your emails.
10. What is an MSA (Mail Submission Agent)?
The Mail Submission Agent (MSA) is the component that prepares your email for delivery after you hit “send.” It ensures your email is formatted correctly and ready for the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) to take over.
11. What is MTA (Mail Transfer Agent)?
A Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) is the software responsible for transferring emails between servers. It uses SMTP to route emails and ensure they reach the correct destination.
12. What is an MDA (Mail Delivery Agent)?
The Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) is the final step in the email delivery process. It takes the email from the MTA and delivers it to the recipient’s inbox. Examples include Procmail and Dovecot.
13. What is SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)?
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the protocol used by MTAs to send and receive emails. It’s the foundation of email transmission, ensuring emails are delivered reliably across the internet.
14. What is MX Records (Mail Exchange Records)?
Mail Exchange (MX) Records are part of the DNS MX Records system. They help MTAs find the correct mail server for delivering emails. When you send an email, the MTA looks up the recipient’s MX records to determine where to send the message.
What to read next
Absolutely! Boost Inbox is compatible with most major email service providers.
The warmup process duration may vary depending on your email volume, but it typically ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks.
Yes, Boost Inbox offers dedicated customer support to assist you throughout the warmup process.
While it's possible, it's best to start the warmup process from the beginning with Boost Inbox for optimal results.
.webp)
